In the ever-evolving world of technology, scalability in cloud computing is like the secret sauce that makes everything better. Imagine your favorite pizza place suddenly doubling its size to accommodate all those late-night cravings. That’s scalability in action! It’s the ability to expand or shrink resources based on demand, ensuring businesses can handle traffic spikes without breaking a sweat—or their budget.
What Is Scalability in Cloud Computing
Scalability in cloud computing refers to the capability to expand or reduce resources based on demand. This feature enables businesses to adapt to varying workloads efficiently. It allows organizations to manage resources effectively, ensuring performance remains optimal even during peak usage periods.
Vertical scalability involves adding resources to a single node, enhancing its capacity. For example, increasing the processing power or memory of an existing server meets higher demands efficiently. Horizontal scalability entails adding more nodes to the cloud environment. This approach distributes workloads across multiple servers, allowing for better resource management.
Elasticity plays a significant role in scalability. It ensures that resources can be adjusted automatically based on real-time needs. This utilization of resources minimizes costs while maximizing performance during fluctuating demand. Businesses often experience rapid changes in their traffic, and having the ability to scale resources up or down can lead to effective cost management.
Cloud providers commonly offer scalable services. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud allow users to increase or decrease their computing resources seamlessly. These platforms provide tools that simplify the scaling process, allowing companies to maintain operational efficiency.
To sum up, scalability stands as a vital characteristic in cloud computing. It empowers organizations to respond dynamically to changing workloads while optimizing operational costs. Ensuring resources can align with varying demands will enhance user experience and improve service reliability.
Types of Scalability
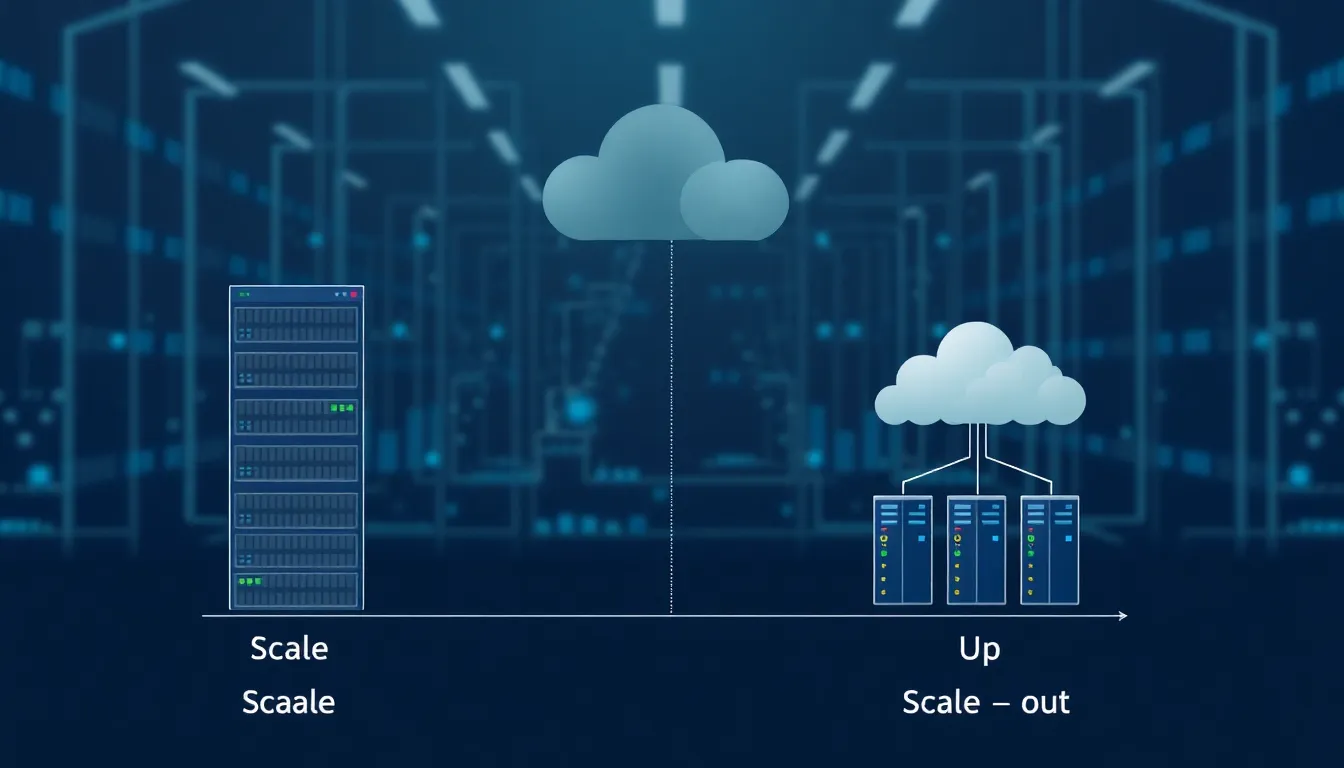
Scalability in cloud computing can be classified into two main types: vertical and horizontal scalability. Understanding these types provides insight into how organizations can effectively manage their resources.
Vertical Scalability
Vertical scalability, often referred to as “scale-up,” focuses on enhancing the capacity of a single server. Increasing memory, processing power, or storage allows one node to handle greater workloads. This approach can simplify management since fewer servers are involved. However, there’s a limit to how much a single machine can be upgraded, which may affect long-term scalability. Applications requiring substantial processing power or memory typically benefit most from vertical scaling. It’s essential to monitor performance and resource usage to ensure that upgrades align with demand as workloads grow.
Horizontal Scalability
Horizontal scalability, also known as “scale-out,” involves adding more servers to distribute workloads across multiple nodes. This approach enhances resource availability and improves redundancy. Organizations can manage high traffic efficiently by deploying additional machines. Load balancers help route requests to different servers, optimizing response times. Setting up new instances can be more cost-effective than upgrading existing hardware. Companies with fluctuating workloads often find horizontal scalability advantageous. Monitoring and automating resource allocation become crucial for maintaining performance and efficiency in a horizontally scaled environment.
Importance of Scalability in Cloud Computing
Scalability plays a critical role in cloud computing, allowing organizations to optimize resource usage as workloads fluctuate. Scalability ensures that businesses can respond efficiently to varying demand without facing downtime. Organizations avoid costly over-provisioning through effective scalability practices.
Efficiency rises significantly when resources adapt in real time to user activities. This dynamic capability enhances performance during peak hours by seamlessly allocating resources where they are most needed. Many cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offer robust scalability features that streamline this process for businesses of all sizes.
Vertical and horizontal scalability each serve unique purposes. Vertical scalability improves performance by enhancing a single server’s capabilities, suitable for applications requiring high processing power. Conversely, horizontal scalability expands resource availability by adding more servers, thereby distributing workloads effectively.
Elasticity complements scalability by enabling automatic adjustments based on real-time requirements, which minimizes costs while maximizing performance. Load balancers play an essential role in managing workloads across multiple servers in horizontally scaled systems, ensuring optimal user experiences.
Investing in scalable cloud solutions leads to sustainable growth. Organizations gain flexibility, allowing them to adapt their infrastructure as needed without significant financial strain. Sound scalability strategies empower businesses to thrive in changing market conditions, optimizing their operational efficiency and enhancing overall user satisfaction.
Challenges of Scalability
Scalability presents several challenges that organizations must address. Resource limitations often emerge as businesses scale, leading to performance bottlenecks. Monitoring resource usage becomes crucial, as inefficient allocation can result in over-provisioning or under-utilization.
Cost management also poses a challenge. While scalability offers flexibility, it’s essential to maintain a balance between scaling resources and controlling expenses. A sudden increase in demand may require organizations to allocate additional funds to support their expanding infrastructure.
Latency issues can arise in horizontally scaled environments. As the number of nodes increases, network performance may degrade, affecting response times. Organizations must implement effective load balancing strategies to mitigate latency and ensure smooth operations.
Maintaining data consistency during scaling activities remains another challenge. When multiple nodes handle requests, ensuring that data remains synchronized can become complex. Using distributed databases and replication strategies can help organizations manage this issue.
Security concerns often heighten as systems scale. With more resources and endpoints, the attack surface expands, making systems more vulnerable to threats. Implementing robust security measures, such as identity and access management, becomes critical in a scalable environment.
Lastly, managing complexity increases as scalability strategies evolve. Organizations face challenges in coordinating multiple services and applications, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. Adopting automation tools and practices can streamline this process, aiding in better resource management.
These various challenges require careful consideration, as overcoming them is essential for leveraging the full benefits of scalability in cloud computing.
Best Practices for Achieving Scalability
Organizations benefit from implementing specific practices for effective scalability. First, leveraging cloud-native architecture enhances flexibility. This approach allows resources to scale dynamically, accommodating varying workloads and user demands.
Next, optimizing application performance is crucial. Developers should focus on coding efficiencies, ensuring applications run smoothly under load. This practice minimizes resource strain and maintains user experience during peak times.
Utilizing auto-scaling features is essential as well. Major cloud providers, like Amazon Web Services, offer auto-scaling options that automatically adjust resources based on real-time demand. By incorporating this feature, organizations minimize manual intervention and reduce the risk of human error.
Monitoring system performance closely aids in identifying bottlenecks. Tools for real-time resource tracking expedite problem detection, facilitating timely responses to performance issues. This practice ensures optimal efficiency and reduces downtime.
Implementing load balancing strategies improves resource distribution across servers. By evenly distributing workloads, organizations enhance system performance and prevent overloading individual servers. This balance is critical for maintaining high availability.
Employing distributed databases can address data consistency challenges. These databases ensure that information remains synchronized across multiple nodes, which mitigates latency issues associated with horizontal scaling.
Enhancing security practices safeguards resources against threats. As scalability increases, so do potential vulnerabilities. Organizations must prioritize robust security measures that adapt to changing infrastructures.
Automating deployment processes streamlines coordination among services. This practice simplifies complexity, reduces errors, and ensures scalability efforts align with operational objectives. Emphasizing automation empowers teams to focus on strategic growth.
Conclusion
Scalability in cloud computing is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in a dynamic environment. By effectively managing resources to match demand, organizations can enhance performance and minimize costs. The choice between vertical and horizontal scalability allows companies to tailor their infrastructure according to specific needs, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
Embracing best practices like cloud-native architecture and auto-scaling features can significantly improve scalability efforts. However, addressing challenges such as latency, data consistency, and security is vital for maximizing the benefits of scalable solutions. With the right strategies in place, businesses can achieve sustainable growth and remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.










